The Business Of Deportation: A Startup Airline's Unusual Strategy

Table of Contents
The Market for Deportation Flights: Unveiling a Hidden Industry
The demand for deportation flights stems from the increasing need for governments to enforce immigration laws and repatriate individuals deemed inadmissible. International agreements and bilateral treaties further fuel this demand, creating a steady stream of contracts for specialized transportation services. The size and growth potential of this market are significant, driven by factors like stricter border controls and evolving immigration policies worldwide.
- Annual Deportations: Estimates suggest millions of deportations globally each year, with significant regional variations depending on immigration policies and refugee flows. Precise figures are difficult to obtain due to the fragmented nature of data collection across countries.
- Key Players: While some major airlines handle deportation flights as a small part of their operations, the market also includes smaller, specialized companies and contractors who often focus exclusively on deportation services. These entities may operate under less scrutiny than larger carriers.
- Government Regulations: The legal framework surrounding deportation transport varies considerably across jurisdictions. International aviation law, national immigration regulations, and human rights conventions all intersect to shape the operating environment for these airlines.
The Startup Airline's Business Model: Costs, Revenue, and Profitability
A startup airline venturing into deportation flights faces a unique cost structure. Initial investments include aircraft acquisition or leasing (often older, more fuel-efficient models are favored for cost-effectiveness), crew salaries (requiring specialized training in security and handling of detainees), fuel, maintenance, insurance (likely higher due to the inherent risks), and robust security measures.
Revenue primarily comes from government contracts, with pricing potentially based on the number of deportees or flight distance. Securing consistent, long-term contracts is crucial for profitability. However, the inherent volatility of government funding and potential for contract cancellations presents significant risk.
- Cost Comparison: Compared to commercial passenger airlines, the cost per passenger is likely higher due to increased security, specialized training, and potentially lower passenger density.
- Profit Margins: Profitability depends heavily on securing favorable contract terms and maintaining efficient operations. Slim margins are anticipated, given the inherent complexities and potential for unforeseen expenses.
- Risk Factors: Geopolitical instability, changes in immigration policies, and the potential for public backlash can significantly impact the profitability and sustainability of this business model.
Ethical Considerations and Public Perception of Deportation Flights
The ethical considerations surrounding deportation flights are profound. Concerns arise regarding the treatment of deportees during transit, including the conditions of the aircraft, access to food and water, and the handling of vulnerable individuals such as children or those with medical needs. The lack of transparency and oversight in some jurisdictions further exacerbates these concerns.
Public perception is often negative, leading to potential protests and negative media coverage. Human rights organizations closely monitor these operations, advocating for improved treatment and greater accountability. The privatization of deportation services fuels the debate, with arguments for efficiency and cost-effectiveness clashing with concerns about human rights and potential abuses.
- Ethical Concerns: Reports of inhumane treatment, overcrowding, and lack of medical attention during deportation flights have fueled ethical debates.
- Public Opinion: Public surveys frequently reveal strong negative sentiment towards the privatization of deportation services, with many believing it undermines human rights.
- Arguments for and Against: While proponents emphasize efficiency and cost-effectiveness, critics highlight the potential for profit to outweigh ethical considerations.
Logistical Challenges and Operational Aspects of Deportation Flights
The logistics of deportation flights are exceptionally complex. Stringent security protocols are required, involving coordination with multiple national authorities, adherence to international regulations, and meticulous planning of flight routes and stopovers. Aircraft suitability (considering passenger capacity and security features) is a key factor, as is the training of flight crews in handling potentially difficult situations. Specialized insurance policies are often necessary to cover the heightened risks involved.
- Logistical Hurdles: Securing landing rights in multiple countries, managing detainee transfers, and dealing with last-minute changes in deportation orders are common challenges.
- Security Measures: Enhanced security protocols, including armed guards on board and strict passenger screening, are crucial aspects of deportation flights.
- Immigration Authority Role: Close collaboration with immigration authorities in both the sending and receiving countries is essential for seamless operations.
The Future of the Business of Deportation
The "Business of Deportation" is a niche market with inherent ethical and logistical complexities. While the demand for deportation flights is likely to remain, the future trajectory will depend heavily on government policies, public pressure, and evolving international norms surrounding human rights and migration. Increased scrutiny and regulation are likely, potentially influencing the business model and operations of companies involved.
The ethical implications are paramount. We need further research and open discussion about the moral and practical consequences of outsourcing such sensitive operations. Engage with this critical issue and consider the broader implications of privatizing the "Business of Deportation." Let's work towards a future where human rights are prioritized in all aspects of international migration.

Featured Posts
-
 Metas Future Under The Shadow Of The Trump Administration
Apr 24, 2025
Metas Future Under The Shadow Of The Trump Administration
Apr 24, 2025 -
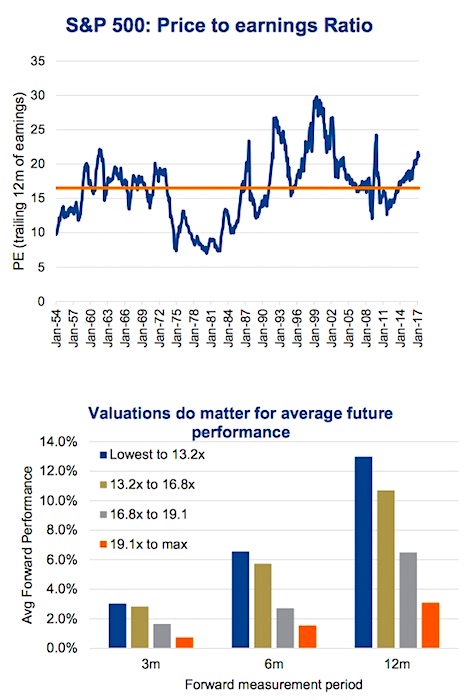 Understanding High Stock Market Valuations Bof As Take For Investors
Apr 24, 2025
Understanding High Stock Market Valuations Bof As Take For Investors
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Houston Isd Mariachi Headed To Uil State Championships After Viral Video
Apr 24, 2025
Houston Isd Mariachi Headed To Uil State Championships After Viral Video
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Sophie Nyweide Mammoth Noah Child Actor Dead At 24
Apr 24, 2025
Sophie Nyweide Mammoth Noah Child Actor Dead At 24
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Harnessing Ai To Create Podcasts From Repetitive Scatological Documents
Apr 24, 2025
Harnessing Ai To Create Podcasts From Repetitive Scatological Documents
Apr 24, 2025
