Optimus Robot Production: Tesla's Challenges With China's Rare Earth Exports
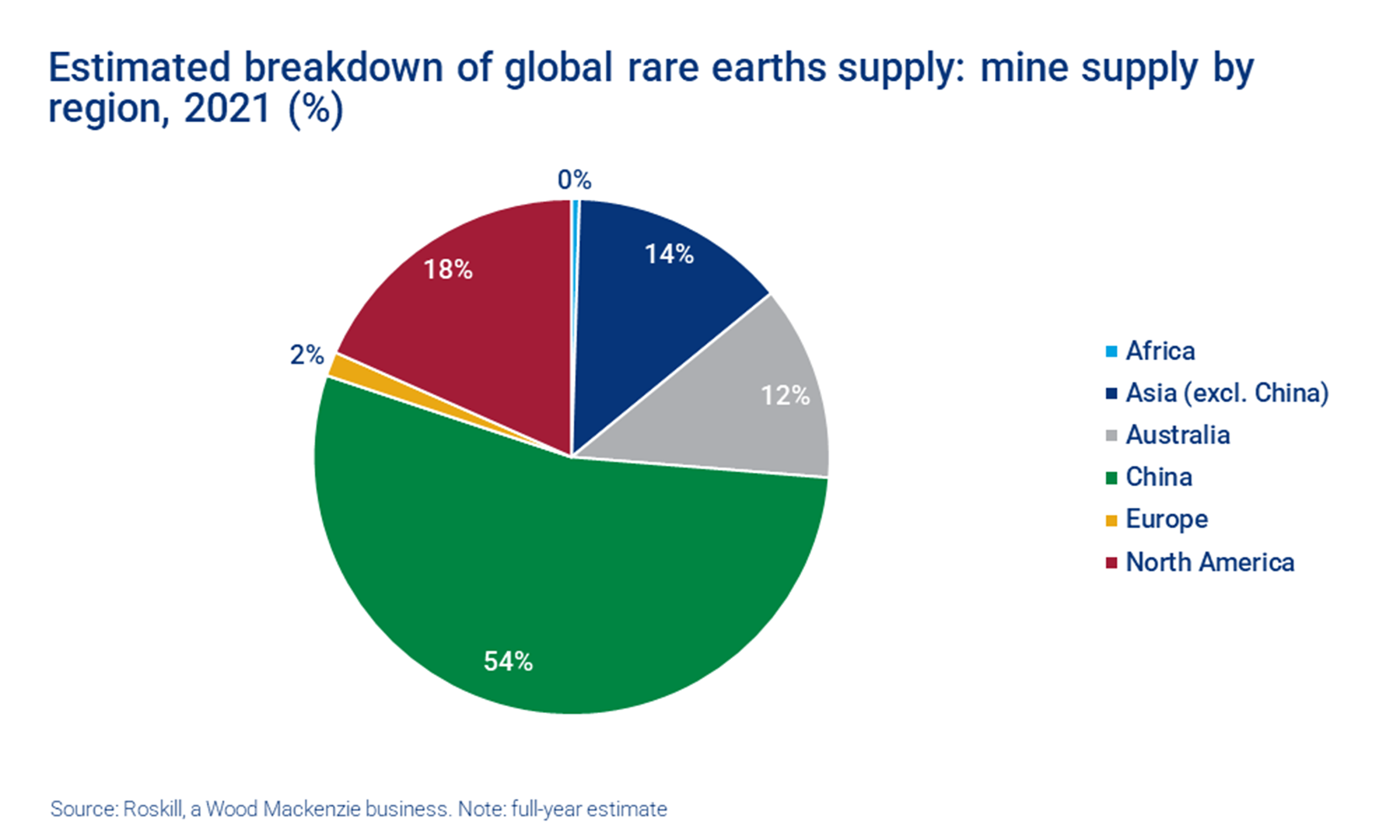
Table of Contents
China's Dominance in Rare Earth Mineral Supply
China's near-monopoly on the rare earth market is a well-established geopolitical reality. This dominance isn't just about market share; it represents considerable leverage in global supply chains. The implications for tech companies like Tesla, heavily reliant on these minerals for advanced technologies, are profound.
- China controls over 60% of global rare earth production, dwarfing the output of other nations. This concentration of power creates vulnerabilities for companies dependent on these materials.
- Specific rare earth elements like neodymium and dysprosium are crucial for the powerful motors and actuators essential to Optimus's functionality. These magnets are essential for achieving the robot's intended power and precision.
- The geographical concentration of rare earth mines, primarily in China and a few other countries, further intensifies the risk of supply chain disruptions. This geographical concentration makes the supply chain vulnerable to geopolitical events.
Political tensions, trade disputes, or unexpected export restrictions from China could severely disrupt the supply of these vital minerals, causing significant delays and cost increases for Optimus robot production.
The Impact on Optimus Robot Component Manufacturing
The implications of China's rare earth dominance extend directly to the manufacturing of key Optimus robot components. Several critical parts rely heavily on these materials:
- Motors and actuators: The heart of the robot's movement relies on powerful, high-precision motors and actuators that depend on rare-earth magnets for optimal performance. Any disruption in the supply of these magnets would directly impact production.
- Sensors and batteries: Many sensors used in the Optimus robot, enabling its perception and navigation capabilities, incorporate rare earth elements. Similarly, advanced battery technologies often rely on these materials for enhanced energy density and performance.
- Electronic control systems: The intricate electronic systems that control the robot's functions also use rare earth materials in various components, ensuring efficient operation.
Relying on a single major supplier for such crucial components carries immense financial risks. Price volatility, potential delays, and the ever-present threat of supply chain disruptions could significantly increase the cost of Optimus robot production and potentially impact Tesla's profitability and competitiveness. Production timelines would undoubtedly be affected by any disruption in the supply of these essential materials.
Tesla's Strategies to Mitigate Supply Chain Risks
Tesla is undoubtedly aware of the vulnerabilities inherent in relying heavily on Chinese rare earth minerals. To mitigate these risks, several strategies are being explored or could be implemented:
- Investing in alternative suppliers: Diversification is key. Tesla could invest in developing relationships with rare earth mining operations in countries like Australia, the USA, and Canada, to create alternative supply sources.
- Developing alternative materials or technologies: Research and development into alternative materials that can replace rare earth elements in key components is crucial for long-term sustainability. This could involve exploring less reliant materials for magnetic applications or finding alternative energy storage solutions.
- Diversifying its supply chain: Tesla needs to expand its network of suppliers, reducing dependence on any single entity. This includes securing multiple sources for rare earth minerals and exploring opportunities to manufacture components in diverse geographical locations.
- Lobbying for policy changes: Advocating for policy changes that encourage domestic rare earth mining and processing in the USA and other countries is essential to strengthen national security and reduce reliance on foreign sources.
The feasibility and effectiveness of these strategies will depend on several factors, including technological advancements, geopolitical stability, and government support.
Geopolitical Implications and Future Outlook for Optimus Robot Production
The geopolitical ramifications of China's control over rare earth minerals are far-reaching. This control creates potential leverage in international relations, impacting trade negotiations and potentially leading to disputes.
- Potential for trade disputes and sanctions: The reliance on China for crucial components could create vulnerabilities to trade disputes and sanctions, directly impacting Optimus robot production.
- Impact on Tesla's global competitiveness: Supply chain disruptions could compromise Tesla's ability to compete effectively in the global robotics market.
- The need for sustainable and ethical sourcing: Ensuring sustainable and ethically sourced rare earth minerals is critical for maintaining a positive environmental and social impact.
Predicting the future of Optimus robot production requires careful consideration of these factors. The long-term viability of the project depends heavily on Tesla's success in diversifying its supply chain and developing innovative solutions to reduce its reliance on Chinese rare earth minerals. Future trends in rare earth mining and processing, as well as advancements in materials science and robotics, will significantly shape the industry's landscape.
Conclusion: Securing the Future of Optimus Robot Production
Tesla's ambitious Optimus robot project faces significant challenges related to the supply of rare earth minerals, largely concentrated in China. Securing a resilient and diverse supply chain is crucial for the long-term success of Optimus robot production and the broader robotics industry. Diversifying supply sources, investing in alternative materials, and advocating for policy changes that promote domestic mining and processing are vital steps. Further research and open discussions on responsible sourcing of rare earth materials and the future of robotics manufacturing are essential to ensure a sustainable and secure future for this transformative technology. We urge readers to explore further resources on responsible sourcing of rare earth minerals to better understand the challenges and opportunities in this critical area.

Featured Posts
-
 John Travoltas Miami Steakhouse Experience A Pulp Fiction Inspired Feast
Apr 24, 2025
John Travoltas Miami Steakhouse Experience A Pulp Fiction Inspired Feast
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Bof A On Stretched Stock Market Valuations A Reason For Investor Calm
Apr 24, 2025
Bof A On Stretched Stock Market Valuations A Reason For Investor Calm
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Hope And Liams Troubles Bridgets Breakthrough A Bold And The Beautiful Recap April 16
Apr 24, 2025
Hope And Liams Troubles Bridgets Breakthrough A Bold And The Beautiful Recap April 16
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Hong Kongs Chinese Stock Market A Rally Fueled By Trade Hopes
Apr 24, 2025
Hong Kongs Chinese Stock Market A Rally Fueled By Trade Hopes
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Middle Managements Impact On Employee Satisfaction And Business Performance
Apr 24, 2025
Middle Managements Impact On Employee Satisfaction And Business Performance
Apr 24, 2025
