Three-Year Decline: Canadian Consumers Less Keen On Electric Vehicles
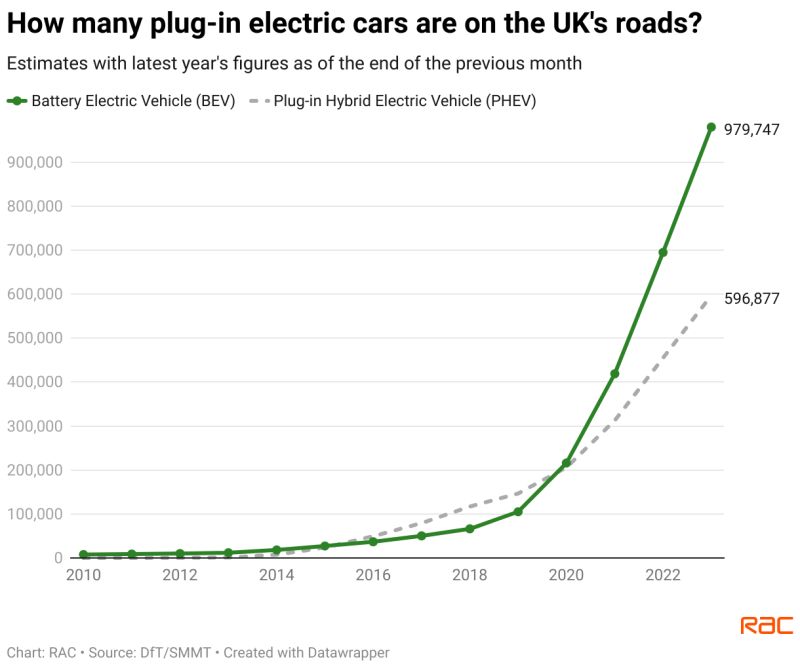
Table of Contents
High Purchase Prices and Limited Affordability
A significant barrier to EV adoption in Canada is the substantial price difference between electric vehicles and comparable gasoline-powered cars. The upfront cost of purchasing an EV remains considerably higher, placing it out of reach for many average Canadian consumers. This affordability gap significantly impacts the market's growth.
- Average EV Prices vs. Gas Car Prices: While the price gap is narrowing, the average price of a new EV in Canada still surpasses that of a similar gasoline-powered vehicle by a considerable margin, often exceeding $10,000.
- Government Incentives and Their Effectiveness: Although the Canadian government offers various incentives, such as rebates and tax credits, their effectiveness in bridging the affordability gap is debatable. Many find the application process complex, and the incentives may not be sufficient to offset the higher initial purchase price.
- Limited Availability of Used EVs and Their Pricing: The used EV market remains relatively small, and the prices of used EVs often don't reflect the significant depreciation seen in gasoline cars, limiting affordability options for budget-conscious buyers.
Statistics from the Canadian Automobile Dealers Association (CADA) and Transport Canada would provide concrete data to further support this analysis of EV affordability in Canada.
Range Anxiety and Charging Infrastructure Gaps
Range anxiety – the fear of running out of battery power before reaching a charging station – significantly impacts EV adoption. Coupled with this is the inadequate charging infrastructure, particularly outside major urban centers. This significantly limits the practicality of EVs for many Canadians.
- EV Range and Typical Canadian Driving Distances: The driving distances between Canadian cities and towns often exceed the range of many currently available EVs, especially in less densely populated regions.
- Current EV Charging Station Network in Canada: While the number of EV charging stations is increasing, the network remains insufficient to support widespread EV adoption, particularly in rural areas and along major highways. The lack of fast-charging options further exacerbates the range anxiety problem.
- Challenges of Charging in Rural Areas and on Long Trips: The scarcity of charging stations in rural and remote areas poses a significant hurdle for potential EV owners, making long journeys impractical or impossible for many.
Lack of Consumer Awareness and Education
A lack of understanding surrounding EV technology, benefits, and maintenance is a crucial factor hindering wider adoption. Many Canadians remain uncertain about the practicalities of owning and maintaining an EV.
- Public Opinion Surveys on EV Knowledge and Misconceptions: Surveys consistently reveal significant misconceptions about EV technology, charging times, and long-term costs.
- Successful EV Awareness Campaigns in Other Countries: Countries like Norway have implemented successful public education campaigns, highlighting the environmental and economic benefits of EV ownership, inspiring increased consumer confidence.
- Improvements to Canadian EV Education Initiatives: Canada needs more comprehensive educational campaigns that address common misconceptions, highlight the benefits of EVs, and provide clear, accessible information on charging infrastructure, maintenance, and government incentives.
Government Policy and Incentives
The effectiveness of current Canadian government incentives requires further evaluation. A comparison with incentives offered in other countries could reveal opportunities for improvement.
- Canadian EV Incentives Compared to Other Countries: Comparing Canada's EV incentives to those in countries like Norway, which boast significantly higher EV adoption rates, could highlight areas for improvement.
- Making Incentives More Accessible and Appealing: Simplifying the application process and potentially increasing the value of rebates could make EV ownership more financially attractive.
- Impact of Carbon Taxes on EV Adoption: The implementation and structure of carbon taxes could be analyzed to understand their impact on EV adoption, potentially revealing ways to better support sustainable transportation choices.
Reversing the Three-Year Decline in Canadian EV Adoption
In summary, the three-year decline in Canadian EV adoption stems from high purchase prices, range anxiety due to charging infrastructure gaps, and a lack of consumer awareness and education. Addressing these interconnected challenges is paramount for stimulating growth in the Canadian EV market. Key to overcoming this "Three-Year Decline: Canadian Consumers Less Keen on Electric Vehicles" is a multi-pronged approach involving increased government investment in charging infrastructure, more comprehensive public education campaigns, and the development of more affordable electric vehicle models.
Addressing the issues of affordability, infrastructure, and consumer education is crucial to reversing this three-year decline and accelerating the adoption of electric vehicles in Canada. Let's work together to make electric vehicles a more viable and appealing option for all Canadians.

Featured Posts
-
 Veroeffentlichung Pne Ag 40 Abs 1 Wp Hg
Apr 27, 2025
Veroeffentlichung Pne Ag 40 Abs 1 Wp Hg
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Motherhood And Victory Bencic In Abu Dhabi Wta Final
Apr 27, 2025
Motherhood And Victory Bencic In Abu Dhabi Wta Final
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Ackmans Trade War Prediction Time Favors Us Hurts China
Apr 27, 2025
Ackmans Trade War Prediction Time Favors Us Hurts China
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Ariana Grandes New Hair And Tattoos A Professionals Perspective
Apr 27, 2025
Ariana Grandes New Hair And Tattoos A Professionals Perspective
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Ohio Train Disaster Long Term Effects Of Toxic Chemicals On Buildings
Apr 27, 2025
Ohio Train Disaster Long Term Effects Of Toxic Chemicals On Buildings
Apr 27, 2025
