Exploring Energy Trade Opportunities: A Canadian Focus On Southeast Asia
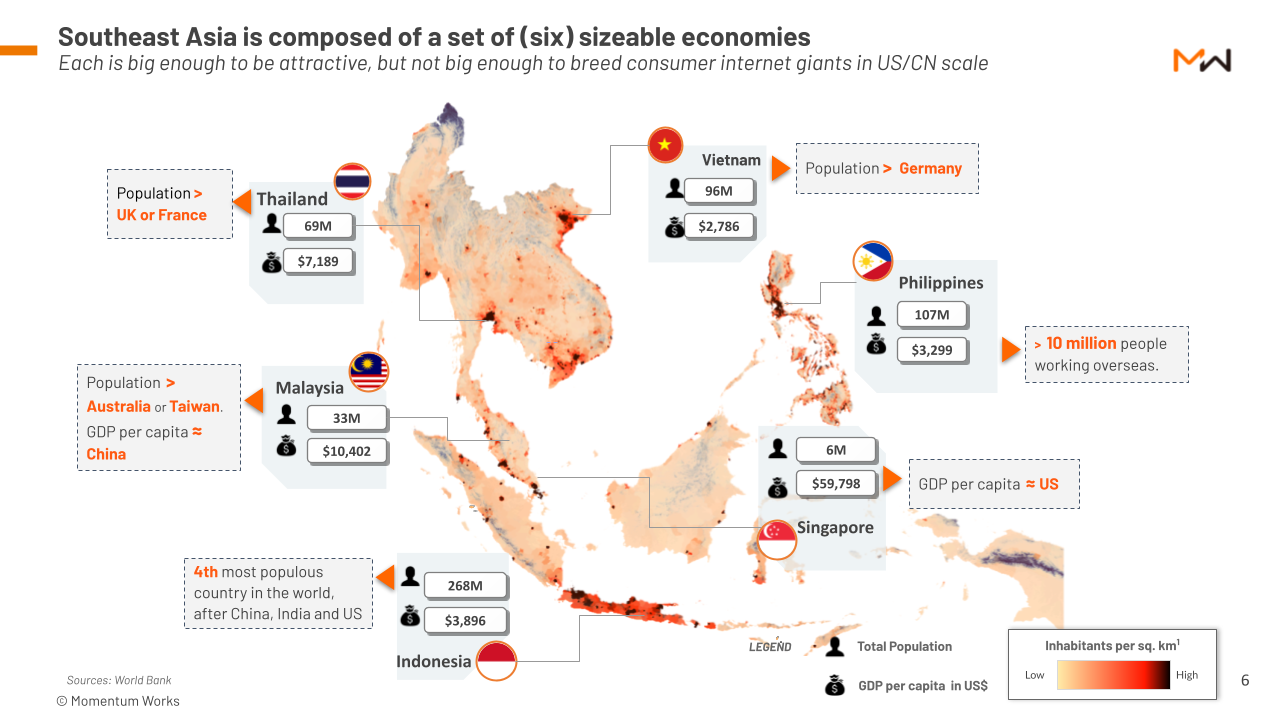
Table of Contents
Canadian Energy Strengths and Southeast Asian Demand
Abundant Canadian Resources
Canada boasts a diverse energy portfolio well-suited to Southeast Asia's needs. Our strengths lie in:
-
Oil and Gas: Canada is a major producer of crude oil and natural gas, particularly liquefied natural gas (LNG), a crucial fuel source for many Southeast Asian nations facing rising energy demands. Canadian LNG can provide a reliable and efficient energy solution, contributing to energy security in the region.
-
Renewable Energy: Canada is a global leader in renewable energy technologies, particularly hydroelectricity, wind power, and solar power. This expertise is highly valuable to Southeast Asian countries aiming to diversify their energy mix and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Canadian companies can offer advanced renewable energy solutions, including project development, technology transfer, and financing.
-
Uranium: Canada is a significant uranium producer, a key component for nuclear power generation. With several Southeast Asian countries operating or planning nuclear power plants, Canadian uranium supplies can contribute to their energy independence and lower carbon emissions.
-
Technological Advancements: Canada's energy sector is known for its technological prowess in extraction, processing, and distribution. This includes innovative techniques for sustainable resource management and clean energy technologies.
-
Specific Examples:
- Canadian LNG to meet rising gas demand in Vietnam.
- Canadian hydropower expertise supporting dam projects in Laos.
- Canadian solar technology contributing to renewable energy initiatives in the Philippines.
Southeast Asia's Energy Needs
Southeast Asia's rapid economic growth and burgeoning population are driving a dramatic increase in energy consumption. This creates significant demand for diverse energy sources:
-
Increasing Energy Consumption: The region's energy needs are outpacing current production capabilities, leading to significant energy deficits. This translates to substantial energy trade opportunities for foreign investors.
-
Specific Energy Deficits: Many Southeast Asian nations face specific energy challenges:
- The Philippines requires substantial investment in renewable energy sources to diversify its energy mix and enhance energy security.
- Indonesia, a large archipelago, requires improved energy infrastructure to connect remote areas and ensure reliable energy access.
- Vietnam's growing industrial sector necessitates a significant increase in natural gas supply.
-
Infrastructure Limitations: The region’s energy infrastructure needs significant upgrades and expansion to meet future demands, creating numerous investment and development opportunities.
-
Key Energy Challenges:
- Inadequate electricity access in rural areas.
- Reliance on imported fossil fuels.
- Limited capacity for renewable energy generation.
- Aging and inefficient energy infrastructure.
Navigating the Regulatory Landscape
Understanding Country-Specific Regulations
Southeast Asia's energy regulatory landscape is diverse and complex, varying significantly across nations. Successful entry requires:
-
Thorough Due Diligence: Canadian companies must conduct comprehensive due diligence, including legal reviews and assessments of local regulations before engaging in any energy projects.
-
Legal Counsel: Employing local legal counsel with deep understanding of the intricacies of each country's energy regulations is paramount.
-
Licensing and Permits: Navigating the process of obtaining licenses and permits for energy projects is often challenging and requires patience and expertise.
-
Regulatory Hurdles and Solutions:
- Environmental impact assessments (EIAs) can be stringent in some countries; thorough preparation and engagement with local stakeholders are essential. (Example: Indonesia)
- Variations in tax regulations and incentives necessitate careful planning.
- Compliance with local content requirements may mandate partnerships with local firms.
International Trade Agreements
Several international trade agreements facilitate energy trade opportunities between Canada and Southeast Asia:
-
Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP): This agreement reduces trade barriers and fosters investment between member countries, offering significant benefits for Canadian energy companies seeking to expand into Southeast Asia.
-
Bilateral Agreements: Exploring opportunities for bilateral trade agreements or enhanced partnerships can further streamline trade and investment flows.
-
Implications of Trade Agreements:
- Reduced tariffs on energy goods and services.
- Enhanced investor protection and dispute resolution mechanisms.
- Streamlined customs procedures.
Building Strategic Partnerships
Collaborating with Local Businesses
Successful entry into the Southeast Asian energy market hinges on strong strategic partnerships:
-
Joint Ventures: Forming joint ventures with local businesses provides access to local expertise, market knowledge, and crucial social and political networks.
-
Strategic Alliances: Collaborations with local firms enhance understanding of cultural nuances and business practices, mitigating risk and improving project success.
-
Advantages of Partnerships:
- Reduced regulatory hurdles.
- Access to local resources and networks.
- Improved community relations and project acceptance.
Government Support and Initiatives
Both Canadian and Southeast Asian governments offer programs supporting international energy partnerships:
-
Canadian Government Initiatives: Export Development Canada (EDC) and other agencies provide financing, insurance, and other support for Canadian companies investing abroad.
-
Southeast Asian Government Initiatives: Many Southeast Asian countries offer incentives and support for foreign investment in their energy sectors, including tax breaks, expedited permitting processes, and infrastructure development programs.
-
Key Government Support Programs:
- Funding opportunities for clean energy projects.
- Tax incentives for foreign investment.
- Government-to-government agreements facilitating energy cooperation.
Conclusion
Southeast Asia presents substantial energy trade opportunities for Canadian companies, offering a chance to export expertise and resources while contributing to the region's energy security. Success requires understanding the regulatory landscape, considering country-specific needs, and establishing strong strategic partnerships. By leveraging their strengths, navigating complexities, and collaborating effectively, Canadian businesses can significantly benefit from the growing energy trade opportunities in Southeast Asia. To explore these energy trade opportunities further and learn more about entering the Southeast Asian market, contact Global Affairs Canada today.

Featured Posts
-
 Zyart Qayd Eam Shrtt Abwzby Wtfqdh Lsyr Aleml Wthnyth Llmnawbyn
Apr 28, 2025
Zyart Qayd Eam Shrtt Abwzby Wtfqdh Lsyr Aleml Wthnyth Llmnawbyn
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Silent Divorce Symptoms How To Know If Your Marriage Is Failing Quietly
Apr 28, 2025
Silent Divorce Symptoms How To Know If Your Marriage Is Failing Quietly
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Aaron Judge Becomes A Father First Child Arrives
Apr 28, 2025
Aaron Judge Becomes A Father First Child Arrives
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Nintendos Action Forces Ryujinx Emulator To Cease Development
Apr 28, 2025
Nintendos Action Forces Ryujinx Emulator To Cease Development
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Analysis Richard Jeffersons Latest Remarks On Shaquille O Neal
Apr 28, 2025
Analysis Richard Jeffersons Latest Remarks On Shaquille O Neal
Apr 28, 2025
